tear film evaluation tests|tear film analysis : agency Schirmer's Test represents a cornerstone in the assessment of tear production, offering insights into the eye's ability to produce both basal and reflex tears. The test involves the strategic placement of a specialized filter .
Electronic Board Repair - Samsof Technologies
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBRoms PSP ~ Tudo para android. 007 - From Russia With Love. Mega. Gdrive. 300 March to Glory. Mega. Gdrive. 50 Cent Bulletproof. Mega. Gdrive. 7th Dragon 2020. Mega. .
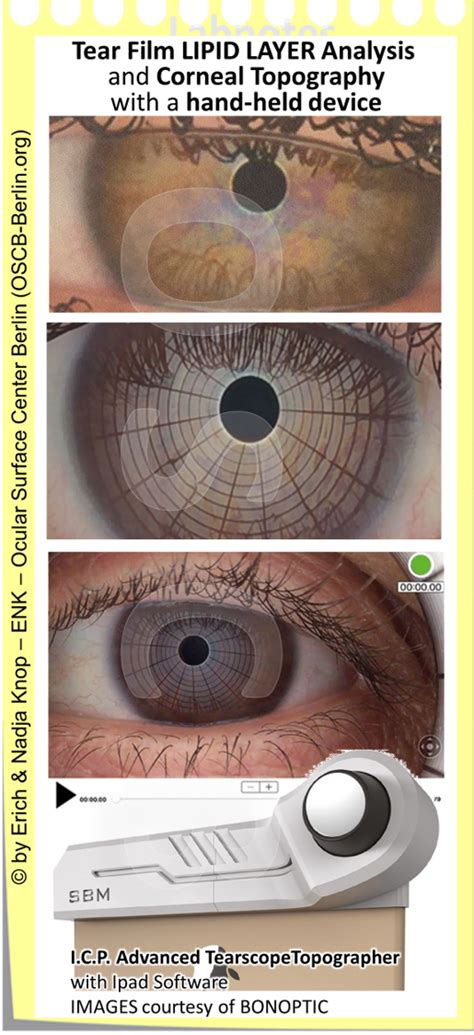
tear film interferometry
puncture & impact testing
The tear film breakup time (tBUT) is a clinical evaluation of evaporative dry eye disease assessed by instilling topical fluorescein into the eyes. In the present study, we . If your tear film does not last long, you may have dry eye. Last updated: January 8, 2021. Your eye doctor can do tests to see if you have dry eye. Learn about the slit lamp test, . Once in the tear film, fluorescein should stay intact for at least 10 seconds. This test provides evidence of tear film stability, which suggests how well the meibomian glands are .Tear film interferometry. Interferometry of the lipid layer of the tear film is a noninvasive method of grading tear film quality and estimating the thickness of the lipid layer, which have been .
Investigators have looked into optical coherence tomography, tear stress tests, fluorescein dye tracking with a xeroscope, and wavefront aberrometry as potential objective methods for diagnosing dry eye.
Schirmer's Test represents a cornerstone in the assessment of tear production, offering insights into the eye's ability to produce both basal and reflex tears. The test involves the strategic placement of a specialized filter . • Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) tear testing. This diagnostic tool helps identify patients with ocular surface inflammation. One study found that the results of the MMP-9 test correlated well with subjective .Common diagnostic methods include consideration of the chief complaint, a questionnaire, a physical examination, a tear film rupture test, corneal punctate staining, and a tear secretion . Tear film osmolarity is quickly becoming an important tool in clinical practice; it’s not only a useful numeric value to obtain as part of a dry eye evaluation, but it’s also great for monitoring treatment progress.
Some are easily accessible to clinicians, while others remain in the field of clinical research. All of these tests provide a better understanding of the pathophysiology of the tear film. This review hopes to provide an overview of the existing tests and their role in evaluating the significance of the tear film in visual function.
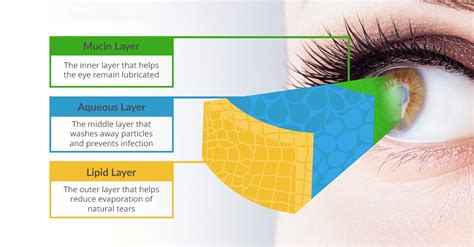
The document summarizes techniques for evaluating the tear film, which has three layers: an outer lipid layer, intermediate aqueous layer, and inner mucous layer. Non-invasive techniques discussed include tear break-up time . Tear break-up time (TBUT) remains one of the most commonly employed tests to assess tear film stability and for dry eye diagnosis [1,2]. First introduced by Norn in 1969, TBUT was defined as the time “interval between . Testing osmolarity Rather than relating vision problems to dryness or irritation, I check the tear osmolarity (TearLab Osmolarity System, TearLab). If the osmolarity is below 308 mOsm/L or there is an inter-eye difference above 8 mOsm/L, then I know that the patient may have dry eye disease, even in the absence of symptoms.
tear film diagram
For Dr. Akpek, after taking the patient’s history, she performs the following minimum battery of tests: tear osmolarity (done by the technician), unanesthetized Schirmer’s test, tear-film breakup time and pattern with fluorescein, corneal fluorescein staining (checking the score after two or two and a half minutes) and conjunctival .Tear film stability can be assessed via a number of tools designed for clinical as well as research purposes. These techniques can give us insights into the tear film, and allow assessment of conditions that can lead to dry eye symptoms, and in severe cases, to significant ocular surface damage and deterioration of vision. Various tests to evaluate tear film such as tear film breakup time, Schirmer's test, Rose Bengal staining, and Phenol Red thread test are described. . External Evaluation Palpebral Aperture Size Blink Patterns Lid Closure Lid Margin Evaluation Lid/punctal Apposition Tear Volume Subjective Tear Meniscus Schirmer Phenol Red Thread .Purpose: To survey practitioners in the tear film/dry eye field for their preferred diagnostic methods for the evaluation of the tear film and dry eye syndrome. Methods: A survey was given to 36 optometrists and 41 ophthalmologists with backgrounds in the area of tear film and dry eye syndrome to find their preferred test if only one diagnostic option was available for tear film .
In the realm of ophthalmology, precise measurement of tear film break-up time (TBUT) plays a crucial role in diagnosing dry eye disease (DED). This study aims to introduce an automated approach .
Tear film osmolarity/MMP-9 test. Measuring tear film osmolarity is regarded as an important further test in the diagnosis of dry eye. A portable osmometer suitable for tear film analysis in routine clinical practice is currently under evaluation in clinical trials (e30, e31). Existing clinical tests such as tear break up time (TBUT) evaluation and Schirmer test have large examiner-based differences with inaccuracies in tear film height and inability to assess lipid layer.
Osmolarity as a single test of tear physiology offers the ability to define and differentiate KCS and “normal” subjects with a . The measurement of tear film osmolarity arguably offers the best means of capturing, in a single parameter, the balance of input and output of the lacrimal system. . NelsonJD, WrightJC. Tear film osmolality . Dry eye is a complex multifactorial disease of the ocular surface and tears. It is associated with ocular surface symptoms and is one of the most common causes for ophthalmologic consultation. Despite their frequent use in clinical practice, the usual tests to evaluate dry eye and ocular surface disease–history of symptoms, tear break-up time (TBUT), .The human tear film is a highly ordered structure consisting of a thin layer of lipid on the surface and a thicker aqueous-mucin phase, which increases in mucin concentration toward the corneal epithelial cell layer. . Tear film evaluation and management in soft contact lens wear: a systematic approach Clin Exp Optom. 2017 Sep;100(5) :438 .The results of tear film breakup (BUT) and Schirmer's I and II tests were retrospectively analyzed on 146 patients undergoing elective blepharoplasty over a 41-month period. These tests were evaluated in conjunction with ocular history, orbital and periorbital anatomy, and Bell's phenomenon in order .
The Schirmer test is historically one of the most common methods for evaluating aqueous tear production. This test is usually performed in a darkened room and involves the bilateral application of the folded end of . The tear film is a thin structure (about 2.0–5.5 µm thick 1,2), extremely sophisticated in functioning and composition with a crucial role in maintaining ocular surface physiology.The .
A systematic evaluation begins with a detailed patient history to elucidate the onset, duration, and severity of symptoms, as well as associated factors such as eye redness, pain, vision changes, or discharge that might suggest conjunctivitis, dacryocystitis, or keratitis. . This test assesses the tear film's stability, as an unstable tear . Introduction. Tear film breakup time measurement is a central component of dry eye assessment. Although topical instillation of sodium fluorescein via impregnated strips is commonly used to visualize breakup, it is recognized that it reduces tear film stability. Recently, the Tear Film and Ocular Surface Society Dry Eye Workshop (TFOS DEWS II) recommended . 1. Introduction. Tear break-up time (TBUT) remains one of the most commonly employed tests to assess tear film stability and for dry eye diagnosis [1], [2].First introduced by Norn in 1969, TBUT was defined as the time “interval between the last complete blink and the presentation of the first appearance of a dry spot or disruption in the tear film” [2], [3]. Conventionally, tear film evaluation includes testing for Tear Break Up Time (TBUT) using sodium fluorescein eye drops and the slit lamp. Assessment of the amount of tears produced by the eye is done by placing a strip of filter paper inside the lower fornix of an anesthetized eye, Schirmer tear test 1 (STT1) [ 13 ].
There are different methods to assess the tear film and two of the most common methods include the Schirmer's test and tear film break-up time . Current patterns in the use of diagnostic tests in dry eye evaluation. Cornea. 2008; 27:656–62. [Google Scholar] 6. Kanellopoulos AJ, Asimellis G. In pursuit of objective dry eye screening clinical .Some are easily accessible to clinicians, while others remain in the field of clinical research. All of these tests provide a better understanding of the pathophysiology of the tear film. This review hopes to provide an overview of the existing tests and their role in evaluating the significance of the tear film in visual function.Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 1.0.0.1174 version, 64-bit edition (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). The following variables were defined: presence or absence of DED, lacrimal film thickness, lacrimal meniscus area and height for right and left eye and the differences between the eyes for the last three variables. The Schirmer tear test (STT) is the most common diagnostic test for assessing aqueous tear production in dogs. 4 Schirmer tear test-1 (STT-1) is performed without topical anesthesia to provide an estimate of the basal and reflex tear production. 4 The distal end of the strip is bent in the plastic cover (to avoid contamination from the examiner .
Ocular Surface Inflammatory Risk Evaluation. TFSE® / NIBUT Tear Film Stability Evaluation / Non-Invasive Breakup Time. ABORTIVE BLINKING. EYE REDNESS. DEMODEX. MEIBOGRAPHY IR. EYE FITNESS TEST. D-BUT (not yet accessible) Additional tests were the Standard Patient Evaluation of Eye Dryness (SPEED) questionnaire, tear meniscus height (TMH), Schirmer 1, tear film thickness (TFT), corneal sensitivity and meibography .
webAn Error Occurred. Parking is currently unavailable. We'll be right back.
tear film evaluation tests|tear film analysis